Frontal Assessment Battery (FAB): Difference between revisions
(Created page with "The '''Rapid Frontal Efficiency Battery (BREF)''' is a specific screening test for dysexecutive disorders commonly used in the evaluation of dementia syndromes, usually in conjunction with a more general test (such as an MMSE). A score below 16 (15 if cultural level < 3 = primary = CEP) is considered abnormal. It can be downloaded with its norms as a pdf : image As a reminder, the suspicion of a dementia syndrome (or of a loss of autonomy or depressive affects in an...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''Rapid Frontal Efficiency Battery (BREF)''' is a specific screening test for dysexecutive disorders commonly used in the evaluation of dementia syndromes, usually in conjunction with a more general test (such as an MMSE). | {{Lien français|Article=Batterie Rapide d'Efficience Frontale (BREF)}}The '''Rapid Frontal Efficiency Battery (BREF)''' is a specific screening test for dysexecutive disorders commonly used in the evaluation of dementia syndromes, usually in conjunction with a more general test (such as an MMSE). | ||
A score below 16 (15 | A score below 16 (15 in the case of cultural level < 3 = primary = CEP) is considered abnormal but is not very specific. <u>A score below 12 has good specificity (Se 77%, Sp 87%) for identifying fronto-temporal dementia if the MMSE is above 24</u> (in other dementias such as Alzheimer's disease, all tests are impaired at a more advanced stage). | ||
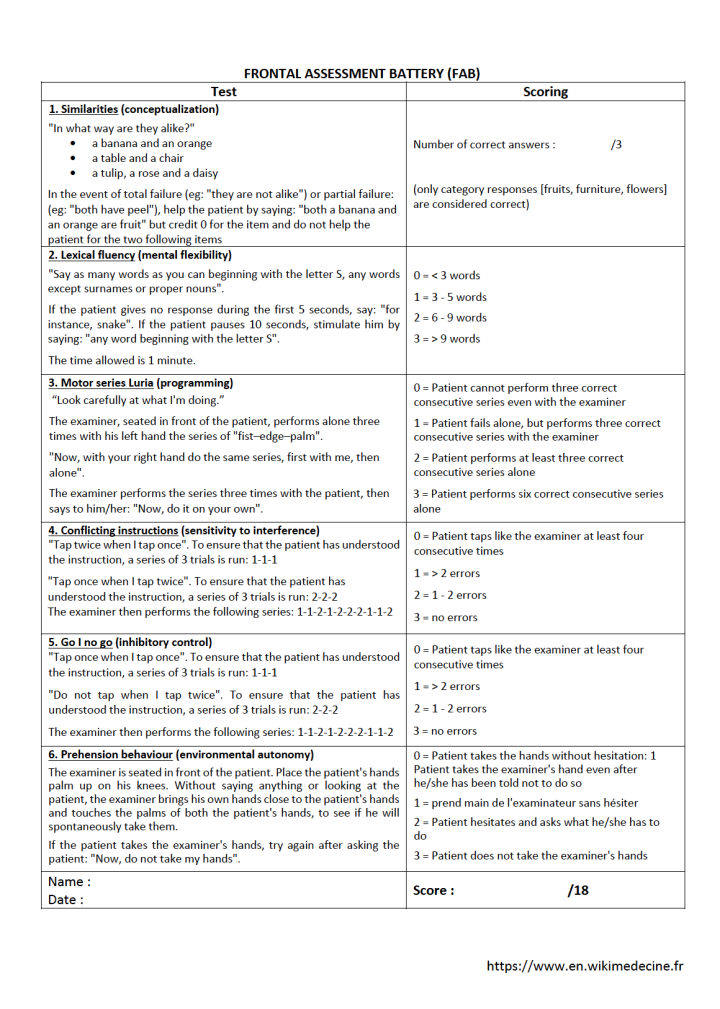
It can be downloaded with its norms as a pdf : | It can be downloaded with its norms as a pdf : | ||
<pdf>File:FAB.pdf</pdf> | |||
[[File:FAB.png|alt=FAB - Frontal Assessment Battery|center|750x1010px]] | |||
As a reminder, the suspicion of a dementia syndrome (or of a loss of autonomy or depressive affects in an elderly patient) should lead to a first-line examination: | As a reminder, the suspicion of a dementia syndrome (or of a loss of autonomy or depressive affects in an elderly patient) should lead to a first-line examination: | ||
| Line 16: | Line 18: | ||
In the event of positive or doubtful results, cognitive testing by a neuropsychologist should be carried out as a second line. | In the event of positive or doubtful results, cognitive testing by a neuropsychologist should be carried out as a second line. | ||
=== Author(s) === | |||
Dr [[User:Shanan Khairi|Shanan Khairi]], MD | |||
=== Bibliography === | |||
Dubois B et al, The FAB: a Frontal Assessment Battery at bedside, Neurology, 2000 Dec 12;55(11):1621-6 | |||
Slachevsky A et al., Frontal Assessment Battery and Differential Diagnosis of Frontotemporal Dementia and Alzheimer Disease, Archives of Neurology, 2004 61(7): 1104-1107 | |||
2015 Review of consensus versions of cognitive tools according to GRECO (Groupe de Réflexion sur les Evaluations Cognitives){{Lien espagnol|Article=Batería de evaluación frontal (Frontal Assessment Battery - FAB)}} | |||
[[Category:Clinical tools]] | |||
[[Category:Neurology]] | |||
[[Category:Geriatrics]] | |||
[[Category:Dementia syndromes]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:37, 7 October 2023
The Rapid Frontal Efficiency Battery (BREF) is a specific screening test for dysexecutive disorders commonly used in the evaluation of dementia syndromes, usually in conjunction with a more general test (such as an MMSE).
A score below 16 (15 in the case of cultural level < 3 = primary = CEP) is considered abnormal but is not very specific. A score below 12 has good specificity (Se 77%, Sp 87%) for identifying fronto-temporal dementia if the MMSE is above 24 (in other dementias such as Alzheimer's disease, all tests are impaired at a more advanced stage).
It can be downloaded with its norms as a pdf :
As a reminder, the suspicion of a dementia syndrome (or of a loss of autonomy or depressive affects in an elderly patient) should lead to a first-line examination:
- A complete history and clinical examination
- Cognitive assessment using MOCA or MSSE + BREF
- A mini-Cog is an acceptable alternative to systematic screening (to be performed annually on all geriatric patients).
- Assessment of autonomy via an IADL (ideally, compare answers with someone close to the patient)
- Affect assessment via a GDS
In the event of positive or doubtful results, cognitive testing by a neuropsychologist should be carried out as a second line.
Author(s)
Dr Shanan Khairi, MD
Bibliography
Dubois B et al, The FAB: a Frontal Assessment Battery at bedside, Neurology, 2000 Dec 12;55(11):1621-6
Slachevsky A et al., Frontal Assessment Battery and Differential Diagnosis of Frontotemporal Dementia and Alzheimer Disease, Archives of Neurology, 2004 61(7): 1104-1107
2015 Review of consensus versions of cognitive tools according to GRECO (Groupe de Réflexion sur les Evaluations Cognitives)